In contrast to aortic or mitral diseases, there has been far less discussion on indications for tricuspid valve repair or replacement. Despite the fact that tricuspid regurgitation (TR) can result in significant symptoms, it remains undertreated. Patients are rarely referred for isolated surgical repair, or replacement, and most surgeries are performed in the context of other planned cardiac surgery. In this article, we will review the causes and natural history of untreated severe TR, indications and surgical approaches for correction of TR.
Causes, Assessment and Natural History
Approximately 80 % of cases of TR are functional due to right ventricular (RV) enlargement resulting in annular dilation, or leaflet tethering.1 RV dilatation is secondary to left heart failure, other valvular causes, RV volume or pressure overload. Less-common causes of TR are organic and include rheumatic, congenital, endocarditis, traumatic/iatrogenic, pacemaker or defibrillator leads interfering with leaflet coaptation, or myxomatous degeneration of the tricuspid valve. A unique cause of TR is isolated TR, the result of marked tricuspid annular dilatation due to degenerative condition of the annulus and/or right atrium.1,2
With TR, patients may experience fatigue and decreased exercise tolerance as a result of decreased cardiac output or the ‘classic symptoms’ of right-sided heart failure from elevated right atrial pressures, such as peripheral oedema, ascites, congestive liver and decreased appetite. Atrial fibrillation is also common as a result of right atrial enlargement. Echocardiography is routinely used to assess the severity of TR in clinical practice. This is performed in an integrative manner using color Doppler, assessing the morphology of continuous wave Doppler recordings across the valve, pulsed wave Doppler of the hepatic veins, measurement of vena contracta width and calculation of effective regurgitant orifice (ERO) using the proximal-isovelocity-surfacearea (PISA) method.3 Serial assessments of TR must be interpreted in the patient’s clinical context, because severity can be affected by multiple factors, such as volume status, respiratory cycle and after-load.4
Without treatment, TR may deteriorate over time, leading to worse symptoms, biventricular heart failure and death. Several trials investigated the impact of TR, in and by itself, or in conjunction with other valvar diseases, on survival and cardiac outcomes.5–8 In a large retrospective analysis of <5,000 patients by Nath et al.,8 it was shown that severe (and even moderate) TR is associated with worse survival even when adjusted for pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), RV size and function. The limitations of all these studies were that the considerable matter of multiple co-morbidities affected survival (severe pulmonary hypertension, poor LV function, organic valve disease right and left-sided), so that it was difficult to prove whether TR in and by itself independently affects survival, or is it a surrogate for associated conditions.
Indications and Timing of Tricuspid Valve Surgery
Because indications for TR surgery differ significantly whether it is performed at the time of left-sided valve surgery, or in isolation, we will discuss them separately.
Isolated Tricuspid Regurgitation Surgery
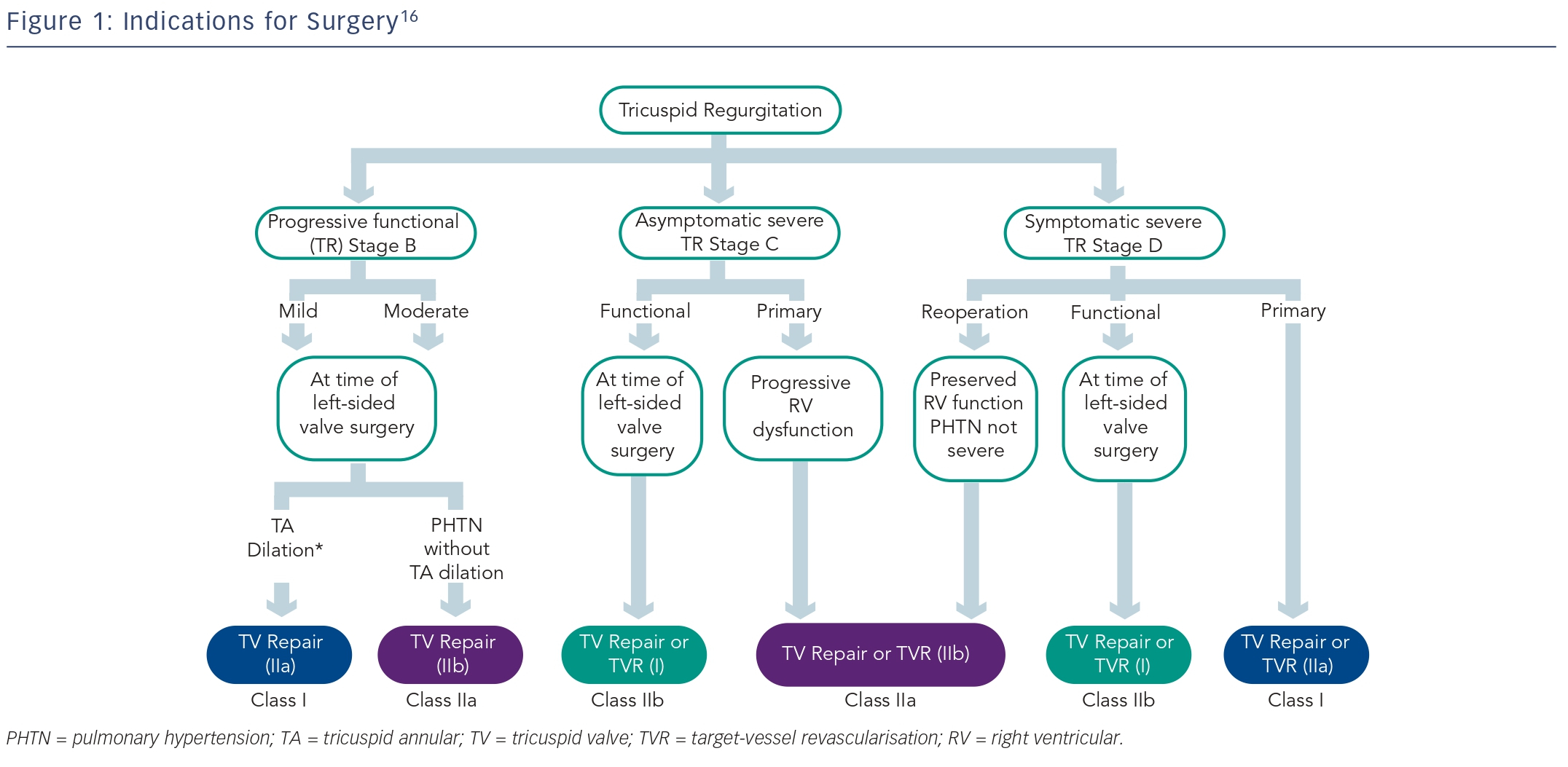
Recently we have shown that severe (ERO >0.4 cm2), isolated (without significant co-morbidities, structural valve disease, significant PASP elevation by Doppler or overt cardiac cause) TR is associated with excess mortality and morbidity,9 thus warranting heightened attention to diagnosis and quantification of TR, and suggesting that it should be treated aggressively. Furthermore, several publications have shown that isolated tricuspid valve surgery can be performed with an acceptable operative mortality if patients undergo surgery before the onset of advanced heart failure symptoms, or severe RV dysfunction.5,10–12 Based on the recent data the practice has evolved to include more surgical treatment of TR even when it is isolated.13 Recent guidelines recommended (Class IIa indication) that isolated tricuspid valve surgery can be performed for patients with symptoms due to severe primary TR, including congestive hepatopathy, preferentially before onset of significant RV dysfunction.14–16 It should be noted that the optimal timing of isolated tricuspid valve surgery for asymptomatic patients with severe TR is controversial. The US guidelines have suggested a conservative approach that includes serial assessments of RV size and function that may indicate the need for corrective surgery (Class IIb indication) in selected patients with severe TR, continued deterioration of RV and low surgical risk. On the other hand, the European recent guidelines16 are more specific since they clearly state “Surgery should be considered in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic patients with severe isolated primary TR and progressive RV dilatation or deterioration of RV function (Class IIa indication).”
Another important and controversial question pertains to whether to re-operate just for severe TR in patients who have undergone previous left-sided valve surgery. Isolated tricuspid valve surgery for severe TR after previous left-sided surgery has historically been performed relatively late in the natural history of the disease, only when patients became severely symptomatic with signs of right heart failure. Because of the delay in surgery, mortality rates for re-operative tricuspid surgery late after left-sided valve surgery have been exceedingly high (10–25 %).14,15 This high mortality was likely related to the advanced nature of RV failure encountered at the time of the second procedure, residual pulmonary hypertension, LV dysfunction and other valve abnormalities. The sobering results seen with tricuspid valve repair at reoperation inject a note of caution into its performance and may encourage replacement with an ageappropriate (mechanical or biological) prosthesis. Recently, several advanced centers of excellence17,18 have reported good peri-operative mortality rates (as low as 4 %), and reasonable long-term outcome with tricuspid valve reoperation when performed early and before severe RV dysfunction occurs. Thus, although the US guidelines15,19 advocate that reoperation for isolated TR may be considered only for persistent symptoms related to TR in patients who have undergone previous left-sided surgery, and the presence of either severe pulmonary hypertension or significant RV dysfunction constitutes a relative contraindication to reoperation, the European guidelines16 are more permissive and recommend surgery in this setting also in asymptomatic patients if there are signs of RV dilatation/dysfunction.
Tricuspid Regurgitation Surgery at the Time of Left-sided Valve Surgery
It is agreed that severe TR of either a primary or functional nature may not predictably improve after treatment of the left-sided valve lesion and reduction of RV after-load.7,14,15 It is also known that adding tricuspid valve repair during left-sided surgery does not add appreciably to the risks of surgery. Furthermore, it was shown that reoperation for severe, isolated TR after left-sided valve surgery is associated with a peri-operative mortality rate up to 25 %.14,15 Thus, because of the hazards imposed by reoperation, the unpredictable nature of TR after successful mitral surgery and the simplicity and low morbidity imposed by adding a cerclage stitch or annuloplasty band on the tricuspid annulus during left-sided surgery have influenced decisionmaking in favour of repair of functional TR initially at the time of leftsided valve surgery. The question remains: when to deal with tricuspid correction during left-sided surgery? Left uncorrected at the time of left-sided valve surgery, moderate and even mild degrees of functional TR may progress over time in approximately 25 % of patients and result in reduced long-term functional outcome and survival.7,20,21 Risk factors for persistence or progression of TR include tricuspid annulus dilatation (>40 mm or 21 mm/m2 on transthoracic echocardiogram [TTE], or >70 mm on direct intra-operative inspection), significant RV dysfunction or dilatation, significant tricuspid leaflet tethering, atrial fibrillation or pulmonary hypertension at the time of left-sided valve surgery, rheumatic or functional aetiology of mitral disease or history of right heart failure.7,20,21 Based on these data the recent guidelines committee has advocated tricuspid valve repair for patients with severe TR (Class I indication), or mild, moderate functional TR at the time of left-sided valve surgery with either tricuspid annular dilatation or prior evidence of right heart failure (Class IIa indication). Furthermore, tricuspid valve repair should be considered (Class IIb indication) in patients with moderate functional TR and pulmonary hypertension at the time of left-sided valve surgery. Nevertheless, not all mitral diseases are similar. In two recent large series from the Mayo Clinic it was shown that in patients who underwent mitral valve repair for isolated degenerative leaflet prolapse that had moderate or less coexistent functional TR at the time of surgery, TR regressed until the third year in the majority of patients following successful and durable degenerative mitral valve repair, irrespective of annular diameter, and only one tricuspid valve repair for severe symptomatic TR was necessary 4.5 years after the initial MV operation.22,23 On the other hand, 29 % of the patients who had 5-year follow up at that study had at least moderate–severe TR at the end of follow up. Based on these data, the indications for tricuspid repair, at the time of mitral repair for mitral valve prolapsed, continue to be debatable. Some believe that early correction of mitral regurgitation for mitral valve prolapsed, without concomitant tricuspid repair, is reasonable because it may diminish the late occurrence of functional TR,24 while others support a more aggressive approach, requiring tricuspid repair whenever the annulus is dilated, similar to patients with functional, or rheumatic, mitral regurgitation.7,16
Repair or Replace
The last factor pertaining to tricuspid valve surgery is whether to replace or repair the valve, how to repair and whether to use a bioprosthetic or mechanical prosthesis whenever we replace. Singh et al. have shown in their seminal report that tricuspid valve repair is associated with better peri-operative, midterm and event-free survival than tricuspid valve replacement, at least in patients with organic tricuspid disease. Despite more TR in the repair group during follow up, reoperation rates and functional class were similar. Thus, it is common practice that repair should be pursued whenever possible in patients with TR.25 In terms of the mode of repair, the debate continues, with most surgeons preferring placement of an annuloplasty ring because it is associated with improved survival and event-free survival compared with De Vega annuloplasties.26,27 Nevertheless, others believe that bi-cuspidisation annuloplasty is equally effective as ring annuloplasty at eliminating TR, but is simpler and less expensive.28
However, the durability of tricuspid valve repair, even when using annuloplasty rings may be limited in some patients. The Cleveland Clinic group has shown that increased preoperative tricuspid leaflet tethering height and area, low LVEF and increased RV pressure were related to worse TR during follow up, and predicted early and mid-term adverse outcomes of ring annuloplasty. Thus patients with significant tethering, significant distortion of the valve, LV and RV dysfunction or severe pulmonary hypertension may require tricuspid valve replacement to avoid long-term repair failure and adverse clinical outcomes. A recent meta-analysis tried to address the question of whether patients requiring tricuspid replacement should have a mechanical or a biological valve. Surprisingly, there were no major differences between the insertion of a mechanical or biological tricuspid valve. The reoperation rate was similar with bio-prosthetic degeneration rate being equivalent to the mechanical thrombosis rate. Conversely, up to 95 % of patients with a bio-prosthesis still received anticoagulation. Survival was equivalent between biological and mechanical valves, thus a mechanical tricuspid prosthesis is reasonable in patients less than 60 years of age who do not have a contraindication to anticoagulation, just like in patients undergoing aortic or mitral valve replacement.29
Conclusions
In the absence of clinical trials, present guidelines are based on expert opinion. The surgical indications for TR are considered more actively if:
- Another cardiac operation is considered, especially at the time of left-sided valve surgery.
- If functional TR is severe, particularly based on quantitative criteria such as ERO ≥40 mm2.
- When the patient is symptomatic from the TR, especially with congestive signs directly related to the TR, or marked reduction of functional capacity measured without other cause than the TR.
Nevertheless, it is essential to consider surgery only if the co-morbid conditions are not overwhelming, RV dysfunction is not irreversible, and life expectancy is at least several years.