Tricuspid regurgitation
The semi-lunar tricuspid valve (TV) is the largest of the four heart valves and its pathology is an important cause of morbidity and mortality, yet treatment options are limited.1,2 As such, the TV is often referred to as the “forgotten valve”.2 Tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is the most prevalent pathology of the TV.2 Mild TR with a structurally normal TV apparatus is common and usually benign, but moderate or severe TR is typically pathologic and can lead to irreversible myocardial damage.1
TR can occur due to primary pathology as well as secondary to atrial or ventricular dysfunction.2,3 Primary disease accounts for 8–10 % of cases of TR in adults, with secondary TR causing the majority of cases.1,3 Secondary TR occurs due to eccentric annular dilatation of the valve and in response to right ventricular (RV) as well as atrial remodelling.3 It can also occur upon chronic volume overload of the RV.3 In secondary TR, the extent and underlying cause of annular dilatation plays a critical role in determining prognosis.4 Regardless of aetiology TR is capable of worsening, so treatment is essential for improving patient outcomes.1
TR occurs in 65–85 % of the population.1 Moderate to severe TR occurs in 14.8 % of men and 18.4 % of women, with 1.6 million patients in the US alone.3-5 Patients with TR have a poor prognosis with high mortality rates, which increase with the severity of TR.5,6 Compared to mild TR, severe TR is a predictor of adverse outcomes, independent of the severity of left ventricular (LV) dysfunction, pulmonary hypertension, RV size and function, or age.2,6
Lack of treatment
Despite the impact of severe TR on morbidity and mortality, treatment of isolated TR is infrequent and, in many cases, not recommended.4,5 Comorbidities (such as LV dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension) can increase mortality risk and should therefore be considered when deciding on treatment.7 As a result of the risks of treating isolated TR, the majority of patients with symptomatic TR are treated pharmacologically, with treatments targeted towards the underlying disease process.4 Diuretics are often administered to address volume overload and lessen the associated symptoms.3
An unsuccessful reduction in symptoms is common with medical therapy; surgery is the next treatment option.2,7,8 The goal of surgery is to repair the TV to reduce annular dilatation and reduce TV leaflet tethering.9 However, surgery is risky, particularly for older patients and those with multiple comorbidities.6,9–10 Mortality rates have been reported at 10 % during isolated TV repair procedures, but significantly higher for TV replacement and repeat procedures.6,12–14 As a result, only a few patients with moderate to severe TR undergo surgery. In the US, 0.5 % of patients undergo surgery each year – equivalent to <8,000 surgical procedures.1,3
Patients with asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic TR are more often considered for surgery.7 Surgery is usually performed alongside treatment of mitral valve disease, and rates of recurrence are low.2,14 However, there is a substantial group of patients for whom mild TR increases in severity following surgery. Repeat surgery has a high mortality rate (10–20 %).2 If surgery is unsuccessful, only a few options remain.10
As a result of the limited treatment options and the challenges of surgery, patients with TR remain largely undertreated.9 This highlights an unmet need for minimally invasive TV-reconstructive treatment.2
Percutaneous procedures are an attractive alternative option to surgery for TR patients.3,8 However, there are physiological challenges of developing effective transcatheter treatment options, including a lack of durable prosthetic valves and difficulties in quantifying improvement following treatment in terms of symptomatic relief and reduced rehospitalisation.2,5 Other challenges in developing transcatheter treatment strategies were summarised by Rodés-Cabau et al, and include the fragility of the TV tissue and the proximity to the right coronary artery, which increases risk of coronary injury.4 TV treatment is especially challenging in patients with multiple cardiac and non-cardiac confounders for morbidity and mortality.2 Despite these caveats, some TV transcatheter devices have been developed and initial results support their efficacy.15,16
Edwards Cardioband™ Tricuspid Valve Reconstruction System
The Edwards Cardioband Tricuspid System is the first commercially available transcatheter therapy specifically for the treatment of TR.17 The therapy involves reduction of tricuspid annular dimensions in the beating heart, guided by fluoroscopy and transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE).15 The Cardioband implant consists of a contraction wire and polyester fabric covering with radiopaque markers attached to an adjustment mechanism.6 A series of anchors secure the implant along the annulus and the implant is contracted to reduce TR.6
As a percutaneous procedure, it is considered an attractive alternative to surgery for patients with TR deemed to be at high surgical risk.8 The Cardioband Tricuspid System has a similar implant technique to the Edwards Cardioband Mitral Reconstruction System and is comparable in concept, shortening the learning curve for previous users.18 The Cardioband Tricuspid System may provide an effective treatment option for patients with TR.17 The system is delivered via a transfemoral approach and is designed to safely and effectively reduce TR through annular reduction.17 It restores the TV to a more functional state, facilitating leaflet coaptation.8 The supra-annular fixation preserves native anatomy, which allows for potential future treatment options, if indicated. The system is designed to address annular dilatation, which is the main physiological cause of functional TR.1,17,18 Annular reduction is enabled through a standardised procedure, based on the patient’s anatomy.15,17 The procedure is supported by fluoroscopy and TEE, enabling real-time adjustment and confirmation of procedural results.8,18
The TRI-REPAIR study
The TRI-REPAIR study aimed to evaluate the performance and safety of the Cardioband Tricuspid System in patients with severe TR.16 The study was conducted as a single arm, multicentre, prospective study in eight sites in Europe.15,18 Thirty patients with severe secondary TR who met the inclusion criteria were included.
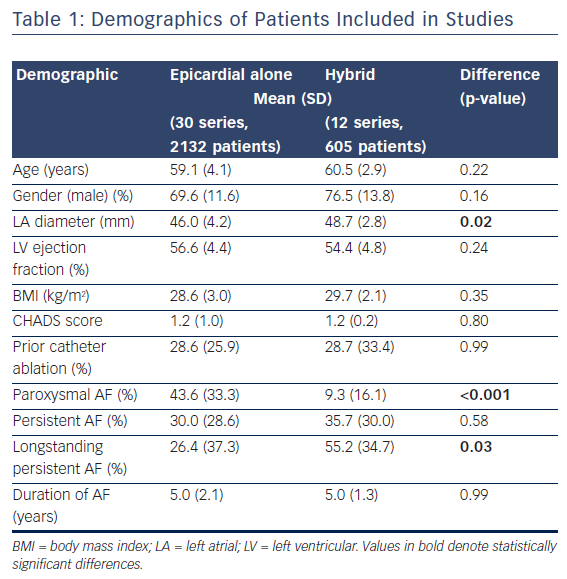
The inclusion criteria were: chronic functional tricuspid regurgitation 2+ to 4+ on a scale of 4+ (moderate to severe), with annular diameter ≥40 mm and valve systolic pulmonary pressure (sPAP) ≥60 mmHg; New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III–Va; symptomatic despite guideline-directed medical therapy, at minimum patient on diuretic regimen; left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥30 % (Table 1).16
Patients were followed up for an initial 30 days, during which time two patients died, with one of the deaths being device-related. At the interim 6-month follow-up, 22 patients remained in the study; there had been one additional death and one patient missed their visit, while four patients’ 6-month visit was still pending.16
The main focus of the study was on the safety and feasibility of the Cardioband Tricuspid System.17 Primary endpoints regarding safety were the overall rate of major serious adverse events, including death, device-related cardiac surgery and serious adverse device effects, until hospital discharge and at 30 days post operation.17 Primary endpoints regarding technical success were the successful access, deployment and positioning of the Cardioband device and septolateral reduction at intraprocedure and discharge.17 Secondary endpoints included TR grade, Effective Regurgitant Orifice Area (EROA) and regurgitant volume (by echocardiography); NYHA classification, performance on the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) and LVEF.17
Findings were positive, with 100 % technical success in terms of access, deployment and positioning of the device, and all patients were successfully implanted with the device.17,19 The safety of the device is supported by the low incidence of procedural and device-related major events, with no adjudicated 30-day events seen in 23 out of 30 patients.15,16 The most common clinical event recorded was bleeding complications (n=4, 13.3 %).16
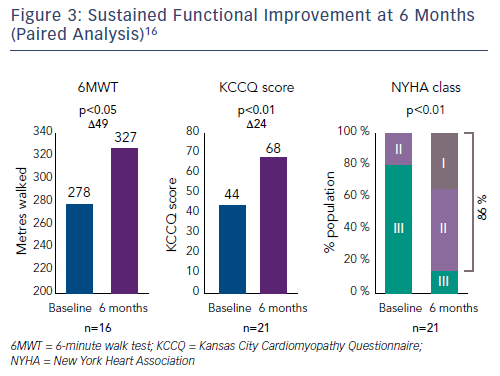
The average reduction in septolateral diameter was 16 %.16,18 This annular reduction was maintained at 6 months (Figure 1).16 Most patients (n=23) achieved lower severity or moderate TR at 30 days, with a number of associated functional and quality of life improvements including increased 6MWT (baseline: 261 m walked, 30 days: 292 m, p=0.076), increased Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) score (baseline: 45, 30 days: 57, p<0.01) and reduced NYHA class (baseline: 0 % class I, 30 days: 82 % class I and II, p<0.01).16
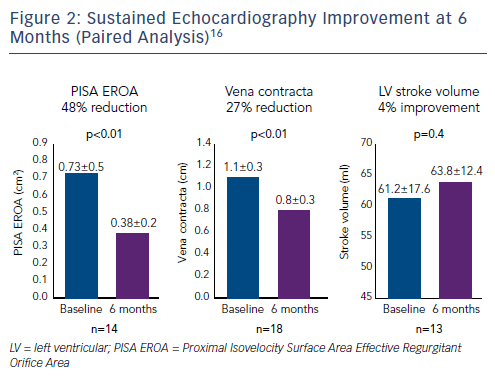
A number of improvements in key echocardiography parameters were recorded at 30 days.16,18 There was a 51 % reduction in Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area EROA (PISA EROA; baseline: 0.79 ± 0.5 cm2, 30 days: 0.39 ± 0.3 cm2, p<0.01), 31 % reduction in vena contracta (baseline: 1.3 ± 0.4 cm, 30 days: 0.9 ± 0.4 cm, p<0.01) and a 9 % improvement in LV stroke volume (baseline: 59.2 ± 19.7 ml, 30 days: 64.5 ± 12.1 ml, p<0.07).16
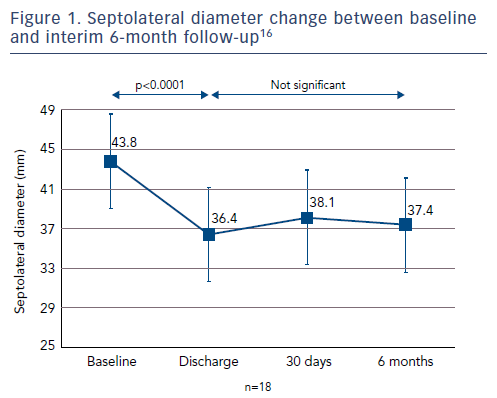
At 6 months, improvements in key echocardiography parameters were sustained (Figure 2), with a 48 % reduction in PISA EROA (baseline: 0.73 ± 0.5 cm2, 6 months: 0.38 ± 0.2 cm2, p<0.01), a 27 % reduction in vena contracta (baseline: 1.1 ± 0.3 cm, 6 months: 0.8 ± 0.3 cm, p<0.01) and a 4 % improvement in LV stroke volume (baseline: 61.2 ± 17.6 ml, 6 months: 63.8 ± 12.4 ml, p=0.04).16 Functional and quality of life improvements were also maintained at 6 months (Figure 3), including 6MWT (baseline: 278 m, 6 months: 327 m, p<0.05), KCCQ score (baseline: 44, 6 months: 68, p<0.01) and NYHA class (baseline: 0 % class I, 6 months: 86 % class I and II, p<0.01). Although the results look promising, further studies are needed to validate the initial results and to understand clinically important endpoints for patients with right-sided heart dysfunction.17,18
Case review
We saw a 78-year-old woman with refractory ascites and oedema, with NYHA functional class III at admission. She was diagnosed with severe TR of secondary aetiology. Her past medical history included coronary artery bypass grafting and mitral valve reconstruction 8 years ago. LV and RV function were moderately impaired. Despite optimal medical therapy, she remained highly symptomatic and required rehospitalisation 5 weeks after discharge.
The heart team excluded the possibility of further open heart surgery, so she was evaluated for transcatheter tricuspid repair. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), TEE and CT were performed, and the anatomy of the TV was considered suitable for repair using the Cardioband Tricuspid System. The implantation of the Cardioband system was straightforward. Contraction of the implant resulted in reduction of the degree of TR from severe to moderate. The patient was discharged on day 5 after the procedure. She improved over the subsequent 6 months, with no further need of rehospitalisation and a marked increase in exercise capacity. Her NYHA functional class improved from grade III to II.
Patient selection for Cardioband Tricuspid System
The Cardioband Tricuspid System is indicated for the reduction of TV regurgitation through direct annuloplasty using an implant.17,19 Patients who could benefit are those with symptomatic TR, deemed either high risk for conventional open heart surgery or who are inoperable.4
In order to optimise the effectiveness of transcatheter tricuspid therapies, accurate patient screening is necessary. Imaging is needed to aid anatomical patient selection, with TEE and TTE considered the most important diagnostic tools to assess the anatomy and pathological details of the valve and to quantify TR.8 Angio-CT and 3D echocardiography are also emerging as potential imaging tools to ease the procedure as well as to select patients.8
Conclusion
Despite the morbidity and mortality associated with pathologies of the TV (such as TR), and the ineffectiveness and risks of current treatment options, the TV so far has received less clinical attention than the aortic and mitral valves.2,9 The prevalence of moderate to severe TR is more than 1.6 million in the US; however, only around 0.5 % of patients with TR are treated, and even fewer receive surgical interventions.3,5,18 Although there have been recent advances in surgery, TV interventions continue to have high risks of morbidity and mortality, and there is a need for effective, minimally invasive treatment options.9,13
The Cardioband Tricuspid System is the first commercially available, dedicated transcatheter therapy for the treatment of TR.17 Results from the TRI-REPAIR feasibility study (n=30) suggest significant echocardiographic, functional and quality of life improvements following implantation of the Cardioband Tricuspid System.
Improvements observed at 30 days and sustained at 6 months included key echo parameters such as PISA EROA, vena contracta, and LV stroke volume, as well as improvements in functional measures such as NYHA class, and quality of life measures such as 6MWT distance and KCCQ score.17,18
Overall, results from the TRI-REPAIR study suggest that the Cardioband Tricuspid System can enable reduction of TR and improve patient outcomes, providing clinicians with a new treatment option for TR.17,18








